树表示由边缘连接的节点。我们将要具体地讨论二叉树或二叉搜索树。
二叉树是用于数据存储目的的特殊的数据结构。二叉树有一个特殊的情况,每个节点可以有两个子节点。二叉树有序数组和链表的两个好处,搜索排序在数组插入或删除操作一样快的,在链表也是尽可能快。
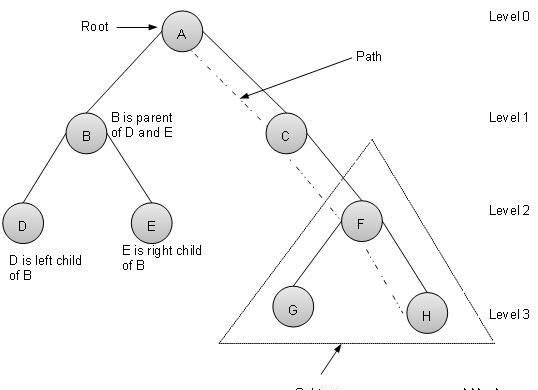
术语
以下是关于树的重要方面。
-
路径 − 路径是指沿一棵树的边缘节点的序列。
-
根 − 节点在树的顶部被称为根。有每棵树只有一个根和一个路径从根节点到任何节点。
-
父子点 − 除根节点的任何一个节点都有一个边缘向上的节点称为父节点。
-
子节点 − 给定节点的边缘部分连接向下以下节点被称为它的子节点。
-
叶子点 − 节点不具有任何子节点被称为叶节点。
-
子树 − 子树代表一个节点的后代。
-
访问 − 访问是指检查某个节点的值在控制的节点上时。
-
遍历 − 遍历意味着通过节点传递一个特定的顺序。
-
层次 − 一个节点的层次表示的节点的产生。如果根节点的级别是0,那么它的下一子结点为1级,其孙子是2级等。
-
键 − 键表示基于一个节点在其上的搜索操作将被进行了一个节点的值。
二叉搜索树表现出特殊的行为。一个节点的左子的值必须低于其父的值,节点的右子节点的值必须大于它的父节点的值。
二叉搜索树表示
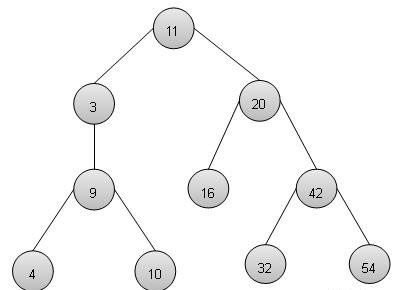
我们将使用节点对象来实现树,并通过引用连接它们。
基本操作
以下是遵循树的基本操作。
-
搜索 − 搜索一棵树中的元素
-
插入 − 插入元素到一棵树中
-
前序遍历 − 遍历树前序方法
-
中序遍历 − 遍历树在序方法
-
后序遍历− 遍历树的后序方法
节点
限定了具有一些数据,引用其左,右子节点的节点。
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
搜索操作
每当一个元素被搜索。开始从根节点搜索后,如果数据小于键值,在左子树中搜索元素,否则在右子树搜索元素。每一个节点按照同样的算法。
struct node* search(int data){
struct node *current = root;
printf("Visiting elements: ");
while(current->data != data){
if(current != NULL)
printf("%d ",current->data);
//go to left tree
if(current->data > data){
current = current->leftChild;
}//else go to right tree
else{
current = current->rightChild;
}
//not found
if(current == NULL){
return NULL;
}
return current;
}
}
插入操作
每当一个元素被插入。首先找到它应有的位置。从根节点开始搜索,那么如果数据小于键值,在搜索左子树空位置并插入数据。否则,在右子树搜索空位置并插入数据。
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL){
root = tempNode;
}else{
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1){
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data){
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL){
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else{
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL){
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
前序遍历
这是一个简单的三个步骤。
- 访问根结点
- 遍历左子树
- 遍历右子树
void preOrder(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL){
printf("%d ",root->data);
preOrder(root->leftChild);
preOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
中序遍历
这是一个简单的三个步骤。
- 遍历左子树
- 访问根结点
- 遍历右子树
void inOrder(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL){
inOrder(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
后序遍历
这是一个简单的三个步骤。
- 遍历左子树
- 遍历右子树
- 访问根结点
void postOrder(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL){
postOrder(root->leftChild);
postOrder(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
}
}
演示程序
TreeDemo.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL){
root = tempNode;
}else{
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1){
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data){
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL){
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else{
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL){
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
struct node* search(int data){
struct node *current = root;
printf("Visiting elements: ");
while(current->data != data){
if(current != NULL)
printf("%d ",current->data);
//go to left tree
if(current->data > data){
current = current->leftChild;
}//else go to right tree
else{
current = current->rightChild;
}
//not found
if(current == NULL){
return NULL;
}
}
return current;
}
void preOrder(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL){
printf("%d ",root->data);
preOrder(root->leftChild);
preOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
void inOrder(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL){
inOrder(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inOrder(root->rightChild);
}
}
void postOrder(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL){
postOrder(root->leftChild);
postOrder(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
}
}
void traverse(int traversalType){
switch(traversalType){
case 1:
printf("\nPreorder traversal: ");
preOrder(root);
break;
case 2:
printf("\nInorder traversal: ");
inOrder(root);
break;
case 3:
printf("\nPostorder traversal: ");
postOrder(root);
break;
}
}
int main() {
/* 11 //Level 0
*/
insert(11);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* |---20 //Level 1
*/
insert(20);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
*/
insert(3);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* |
* |--42 //Level 2
*/
insert(42);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* |
* |--42 //Level 2
* |
* |--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(54);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* |
* 16--|--42 //Level 2
* |
* |--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(16);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* |
* 16--|--42 //Level 2
* |
* 32--|--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(32);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* | |
* |--9 16--|--42 //Level 2
* |
* 32--|--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(9);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* | |
* |--9 16--|--42 //Level 2
* | |
* 4--| 32--|--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(4);
/* 11 //Level 0
* |
* 3---|---20 //Level 1
* | |
* |--9 16--|--42 //Level 2
* | |
* 4--|--10 32--|--54 //Level 3
*/
insert(10);
struct node * temp = search(32);
if(temp != NULL){
printf("Element found.\n");
printf("( %d )",temp->data);
printf("\n");
}else{
printf("Element not found.\n");
}
struct node *node1 = search(2);
if(node1 != NULL){
printf("Element found.\n");
printf("( %d )",node1->data);
printf("\n");
}else{
printf("Element not found.\n");
}
//pre-order traversal
//root, left ,right
traverse(1);
//in-order traversal
//left, root ,right
traverse(2);
//post order traversal
//left, right, root
traverse(3);
}
如果我们编译并运行上述程序,那么这将产生以下结果 -
Visiting elements: 11 20 42 Element found.(32) Visiting elements: 11 3 Element not found. Preorder traversal: 11 3 9 4 10 20 16 42 32 54 Inorder traversal: 3 4 9 10 11 16 20 32 42 54 Postorder traversal: 4 10 9 3 16 32 54 42 20 11
