原型设计模式有助于隐藏该类创建实例的复杂性,在对象的概念将与从头创建的新对象的概念不同。
如果需要,新复制的对象可能会在属性中进行一些更改。这种方法节省了开发产品的时间和资源。
如何实现原型模式?
现在让我们看看如何实现原型模式。代码实现如下 -
import copy
class Prototype:
_type = None
_value = None
def clone(self):
pass
def getType(self):
return self._type
def getValue(self):
return self._value
class Type1(Prototype):
def __init__(self, number):
self._type = "Type1"
self._value = number
def clone(self):
return copy.copy(self)
class Type2(Prototype):
""" Concrete prototype. """
def __init__(self, number):
self._type = "Type2"
self._value = number
def clone(self):
return copy.copy(self)
class ObjectFactory:
""" Manages prototypes.
Static factory, that encapsulates prototype
initialization and then allows instatiation
of the classes from these prototypes.
"""
__type1Value1 = None
__type1Value2 = None
__type2Value1 = None
__type2Value2 = None
@staticmethod
def initialize():
ObjectFactory.__type1Value1 = Type1(1)
ObjectFactory.__type1Value2 = Type1(2)
ObjectFactory.__type2Value1 = Type2(1)
ObjectFactory.__type2Value2 = Type2(2)
@staticmethod
def getType1Value1():
return ObjectFactory.__type1Value1.clone()
@staticmethod
def getType1Value2():
return ObjectFactory.__type1Value2.clone()
@staticmethod
def getType2Value1():
return ObjectFactory.__type2Value1.clone()
@staticmethod
def getType2Value2():
return ObjectFactory.__type2Value2.clone()
def main():
ObjectFactory.initialize()
instance = ObjectFactory.getType1Value1()
print "%s: %s" % (instance.getType(), instance.getValue())
instance = ObjectFactory.getType1Value2()
print "%s: %s" % (instance.getType(), instance.getValue())
instance = ObjectFactory.getType2Value1()
print "%s: %s" % (instance.getType(), instance.getValue())
instance = ObjectFactory.getType2Value2()
print "%s: %s" % (instance.getType(), instance.getValue())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
执行上面程序,将生成以下输出 -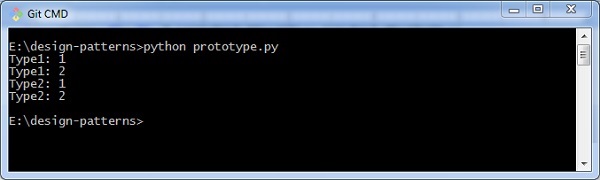
输出中,使用现有的对象创建新对象,并且在上述输出中清晰可见。
上一篇:
构建器(Builder)设计模式
下一篇:
门面(Facade)设计模式
