Python for 迴圈語句
Python for迴圈可以遍歷任何序列的專案,如一個列表或者一個字串。
語法:
for迴圈的語法格式如下:
for iterating_var in sequence: statements(s)
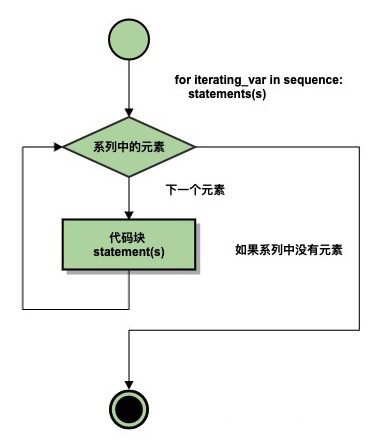
流程圖:
實例:
實例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
for letter in 'Python': # 第一個實例
print '當前字母 :', letter
fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'mango']
for fruit in fruits: # 第二個實例
print '當前水果 :', fruit
print "Good bye!"
以上實例輸出結果:
當前字母 : P 當前字母 : y 當前字母 : t 當前字母 : h 當前字母 : o 當前字母 : n 當前水果 : banana 當前水果 : apple 當前水果 : mango Good bye!
通過序列索引迭代
另外一種執行迴圈的遍曆方式是通過索引,如下實例:
實例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
fruits = ['banana', 'apple', 'mango']
for index in range(len(fruits)):
print '當前水果 :', fruits[index]
print "Good bye!"
以上實例輸出結果:
當前水果 : banana 當前水果 : apple 當前水果 : mango Good bye!
以上實例我們使用了內置函數 len() 和 range(),函數 len() 返回列表的長度,即元素的個數。 range返回一個序列的數。
迴圈使用 else 語句
在 python 中,for … else 表示這樣的意思,for 中的語句和普通的沒有區別,else 中的語句會在迴圈正常執行完(即 for 不是通過 break 跳出而中斷的)的情況下執行,while … else 也是一樣。
實例
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
for num in range(10,20): # 迭代 10 到 20 之間的數字
for i in range(2,num): # 根據因數迭代
if num%i == 0: # 確定第一個因數
j=num/i # 計算第二個因數
print '%d 等於 %d * %d' % (num,i,j)
break # 跳出當前迴圈
else: # 迴圈的 else 部分
print num, '是一個質數'
以上實例輸出結果:
10 等於 2 * 5 11 是一個質數 12 等於 2 * 6 13 是一個質數 14 等於 2 * 7 15 等於 3 * 5 16 等於 2 * 8 17 是一個質數 18 等於 2 * 9 19 是一個質數
更多實例:python 列印菱形、三角形、矩形
